testicular torsion reflex test|cremasteric reflex positive means : online sales Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing or . WEB3 de out. de 2023 · Léo Gregório. A cantora e ex-BBB Gabi Martins, de 26 anos de idade, e a influencer Ayarla Souza, de 22 anos, 'quebraram a web' com vídeos dançando de .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Kiko Roleta de Treino - Kiko Pancada Na Roleta
The cremasteric reflex appears to play a role in preserving thermoregulation of the testicles as part of spermatogenesis. The reflex raises and lowers the testicles to control their .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding testicle. Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing or . Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding testicle.
Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical . Time is Testes. Historically, we thought the time window for possible salvage and survival of a torsed testicle is 6-8 hours. However, more recently it has been recognized that survival percentages are significant . The finding of an ipsilateral absent cremasteric reflex is the most accurate sign of testicular torsion. Torsion of the appendix testis is more common in children than testicular.
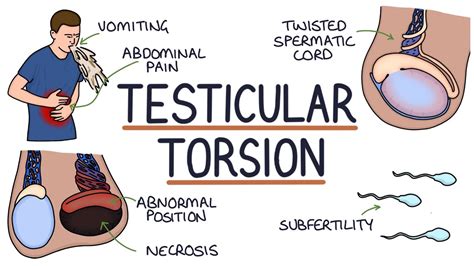
The best predictors for torsion include vomiting, testicular swelling, a firm testicle, a high–riding testicle, and an absent cremasteric reflex. A torsed testicle is only viable for about 4–6 hours after the event. The cremasteric reflex is most commonly performed in the evaluation of acute scrotal pain and the assessment for testicular torsion that is commonly associated with an apparent loss of the reflex. Anatomy . The cremaster muscle is a paired structure made of thin layers of striated and smooth muscle.
In some males this reflex may be exaggerated which can occasionally lead to a misdiagnosis of cryptorchidism. [3]The cremasteric reflex may be absent with testicular torsion, upper and lower motor neuron disorders, as well as a spine injury of L1-L2. It can also occur if the ilioinguinal nerve has accidentally been cut during a hernia repair. [4]The cremasteric reflex can be .
Testicular torsion causes your testicle to twist and cuts off its blood supply. It causes severe pain and requires emergency care. . What tests will be done to diagnose testicular torsion? Your healthcare provider may order a scrotal ultrasound to determine if blood is flowing within your testicular tissues. A scrotal ultrasound is a quick .A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes). Testicular torsion: In cases of testicular torsion, a condition where the testicle twists upon its blood supply, the cremasteric reflex is typically absent or reduced on the affected side. This finding can aid in the diagnosis of testicular torsion and . Sensitivity of cremasteric reflex in testicular torsion varies, ranging as low as 60% 6,7; Testicular lie is often difficult to determine, . is the first-line imaging test recommended to rule in or out testicular torsion and should only be performed before surgical consult when patients with testicular pain have reassuring findings on history .
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . clinical features (pain lasting less than 24 hours, nausea and/or vomiting, abnormal cremasteric reflex, and high position of the testis) were predictive with no false positives reported, thus .
testicular torsion signs on examination
Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 18. Previous testicular torsion. If you've had testicular pain that went away without treatment (intermittent torsion and detorsion), it's likely to occur again. The more frequent the bouts of pain, the higher the risk of testicular damage. Family history of testicular torsion.
1: Epididymis 2: Head of epididymis 3: Lobules of epididymis 4: Body of epididymis 5: Tail of epididymis 6: Duct of epididymis 7: Deferent duct (ductus deferens or vas deferens). Prehn's sign (named after urologist Douglas T. Prehn) [1] is a medical diagnostic indicator that was once believed to help determine whether the presenting testicular pain is caused by acute .Testicular torsion has an annual incidence of approximately 1 in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. 1 It is more common in children and adolescents, and delayed repair can result in the loss of .This video provides a demonstration of how to assess the cremasteric reflex in the context of testicular examination. The absence of the cremasteric reflex c.
Testicular torsion is a challenging and time-sensitive diagnosis that is encountered frequently in daily practice, especially in the emergency room. . Absence of cremasteric reflex Acute onset of symptoms: Testicular appendix torsion: Blue dot sign observed through scrotum . respectively. With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test .
Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity.The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis. Prehn’s test is used to differentiate testicular pain caused by acute epididymitis and testicular torsion. The test involves elevating the testes to assess the impact on testicular pain. . Loss of the cremasteric reflex is associated with testicular torsion, but it should not be relied upon in isolation for ruling the condition in or out . Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency, as without treatment the affected testicle will infarct within hours. . the cremasteric reflex is absent and pain continues despite elevation of the testicle, . can be used to . Testicular torsion is a time sensitive, . Loss of cremasteric reflex. Previously thought to be 100% sensitive and highly specific; 30% of males with normal testicles will have an absent cremasteric reflex ; Studies report varying sensitivities as low as 60% (Mellick 2012)
The cremasteric reflex is a superficial reflex present in males. The female equivalent of this test is called the Geigel reflex. It evaluates the function of the cremasteric muscle which is supplied by the genitofemoral nerve (L1, L2).[1] . Recent abdominal surgery, scrotal pain, and testicular torsion may impair the reliability of the . A neonatal boy is brought to his pediatrician for concern of a blue mass in the scrotum. His parents noticed this an hour ago. On physical exam, the scrotum is blue and firm with some erythema.Absent cremasteric reflex: 1 Nausea or vomiting: 1 High-riding testicle: 1 PPV 100% when >5 points (Suggesting stat urological consult) . ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of .
Testicular torsion must be considered in any patient who complains of acute scrotal pain and swelling. . a thorough physical examination and appropriate diagnostic tests. The onset, character . Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . no adjunctive test should preclude definitive treatment. . A proposed hypothesis for post-torsion reduction of contralateral testicular vitality is that torsion may result in reflex . cremasteric reflex. Imaging with . duplex ultrasound. of the . scrotum. may be required if the . clinical diagnosis. is in doubt. If testicular torsion is suspected, prompt surgical exploration within six hours of symptom onset is essential to salvage the . testis. Important differential diagnoses, e.g.,Studies show that the absent cremasteric reflex may have less than 90% sensitivity and specificity in diagnosing testicular torsion. 1,2,6,7 This large inconsistency makes it unsuitable as an adequate screening or diagnostic test on its own merit. 3
Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates around the spermatic cord, which provides blood to the scrotum (a bag of skin that contains the testicles). . Upon physical examination, the cremasteric reflex is absent. Normally, the cremasteric reflex can be triggered by stroking of the upper inner part of the thigh, which provokes . Testicular torsion in older men: It must always be considered. Urol Case Rep. 2018; 21:1-2. Ciftci AO, Senocak ME, Tanyel FC, et al. Clinical predictors for differential diagnosis of acute scrotum. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2004;14(5):333Y338. Paul EM, Alvayay C, Palmer LS. How useful is the cremasteric reflex in diagnosing testicular torsion .Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become . An absent cremasteric reflex is suggestive of testicular torsion (odds ratio = 7.8), whereas the reflex is preserved with epididymitis. 10 – 12 Torsion of the appendix testis is classically .
testicular torsion physical exam findings
webAutoatendimento via WhatsApp +55 11 4935-2720 Capitais e regiões metropolitanas. SAC - Dúvidas, Reclamações e Orientações Onde estamos. Av. Chedid Jafet, 75. Torre Sul. . A XP exime-se de toda e qualquer responsabilidade por prejuízos, diretos ou indiretos, que decorram da utilização deste material, não concedendo nenhuma garantia .
testicular torsion reflex test|cremasteric reflex positive means